Terminology Of Engine Components
Internal combustion engines are extremely complex and feature a wide array of components that rotate, move up and down, pump, seal, or remain stationary. When repairing or rebuilding your engine, you will come across many different terms when referencing repair manuals and ordering parts. We know it can be confusing, especially when the repair is complex. Even if you are paying a professional to do the work, it's good to be conversant with the topic. In order to help you understand the terminology of engine components, we've created the following glossary, listed in alphabetical order.

Note that this glossary is limited to definitions of “internal” engine components. These are parts contained within the engine block, cylinder head, and crankcase. In contrast, external engine parts are bolted on to the outside of the block (see our related Glossary Of Engine External Parts for definitions regarding such components).
Balance Shaft
Balance shaft – a counterweighted engine shaft that offsets unwanted crankshaft vibrations by rotating in the opposite direction. In our Balance Shafts & Components section, we also offer related hardware such as shaft seals, individual counterweights, replacement sleeves, and more.

Bearing
Bearing – A curved metal piece that allows motion between components with minimum wear and friction. A bearing that surrounds a shaft may be circular in shape (camshaft bearing), or semi-circular (connecting rods, crankshaft), in which case it is also known as a bearing shell. Also see Main bearings and Rod bearings. In our section for Bearings & Components, we’ve got camshaft bearings, crankshaft main bearings, connecting rod bearings, balance shaft bearings, auxiliary shaft bearings, and much more.

Bearing Cap
Bearing cap – A retainer, held in place by nuts and bolts, which secures bearing shells in place.

Camshaft
Camshaft – A shaft in the engine connected to the crankshaft via gears, belts, or a chain, which contains a series of cams to open and close intake and exhaust valves. We also stock related camshaft hardware such as sleeves, bolt lock plates, end caps, dowel pins, o-rings, seals, oil line fittings, oiler control valves, retainer clips, thrust buttons & plates, and much more.

Camshaft Follower
Camshaft follower – See valve lifter.
Camshaft Plug
Camshaft plug – A cup-shaped seal that’s pressed into the back of the engine block where the rear of the camshaft is located. This prevents external oil leaks from a camshaft.

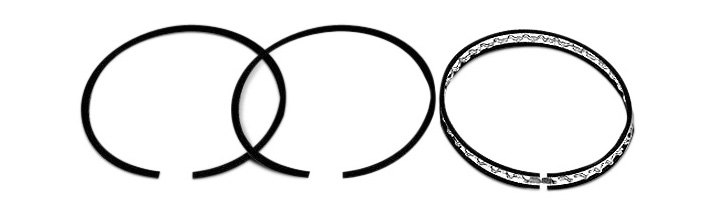
Compression Ring
Compression ring – The piston ring which forms a seal with the cylinder wall to prevent compression loss or gas blow-by (also see piston rings).

Connecting Rod
Connecting rod – The piece which forms the mechanical link between the piston and crankshaft, converting the piston's up-and-down motion into the crankshaft's rotary motion. Related hardware pieces include connecting rod nuts and bolts.

Crankcase
Crankcase – The lower portion of the engine block that encloses and supports the crankshaft, including an oil pan in most cases.

Crankshaft
Crankshaft – The engine's main shaft that rotates after being driven by up-and-down piston motion. At the rear of the crankshaft is an external flywheel, which transfers power to the transmission. On our crankshaft & components main page, we offer related hardware pieces such as lock keys, seals, seal retainers, spacers, thrust washers, and more.
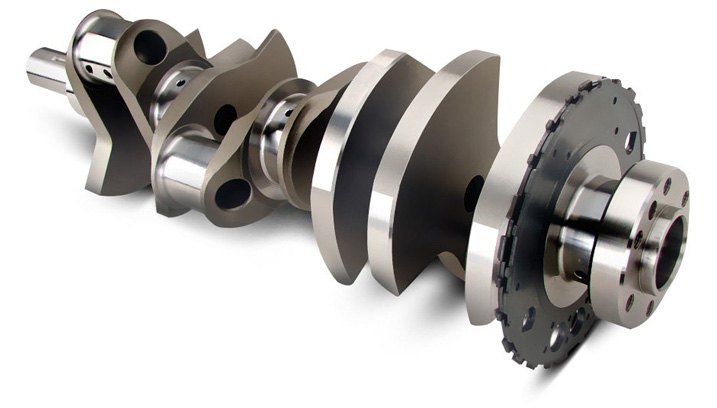

Crankshaft Hub
Crankshaft hub – a specially-shaped metal piece that fits onto the front of the crankshaft. Mounted externally, the hub serves as the mounting point for a harmonic balancer.

Cylinder
Cylinder – The hollow tubular space inside an engine block where piston travel occurs.

Cylinder Head
Cylinder head – The upper engine section that provides a top to enclose the cylinders, and which houses the valves, spark plugs, and overhead camshafts. In our Cylinder Heads & Components section, we’ve got related parts such as studs, dowel pins, fitted nuts, plugs, seals, washers, and more.
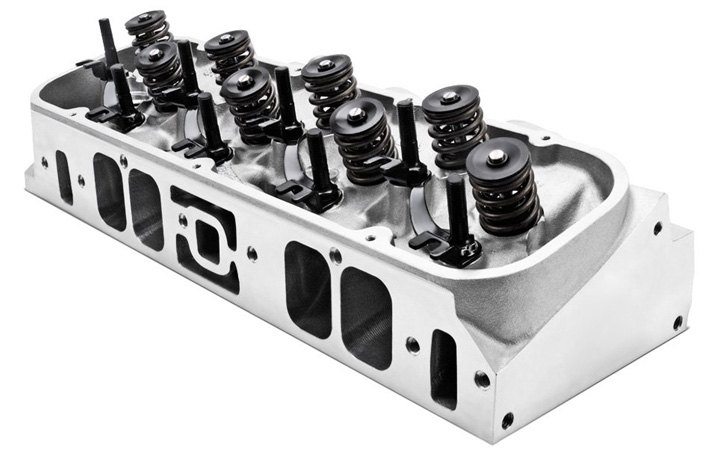

Cylinder Head Bolts
Cylinder head bolts – Bolts used to secure a cylinder head and gasket to the engine block underneath (also known as head bolts).

Cylinder Head Gasket
Cylinder head gasket – A flat gasket typically made of layers of steel, rubber, and other materials, placed between the cylinder head and engine block to maintain a seal as oil and coolant move through the engine, and as both components expand and contract. Also known as a head gasket.

Cylinder Head Shim
Cylinder head shim – Positioned above or below the cylinder head gasket, these are wafer-flat spacer pieces that move cylinder heads slightly higher – restoring valve clearance, valve train geometry, engine compression, and timing to proper specs if cylinder head and/or block surfaces have been resurfaced below factory limits.

Cylinder Liner
Cylinder liner – A replaceable, hollow tube that fits into the cylinder bore or sits within the crankcase, inside which the piston moves up and down (also known as a cylinder sleeve).

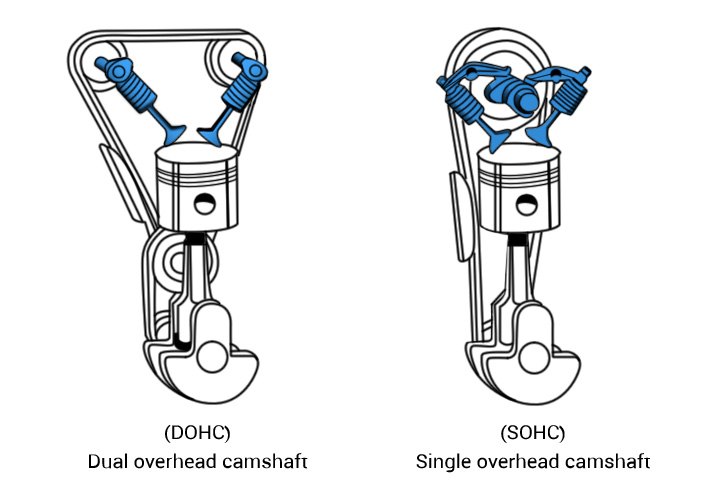
Dual Overhead Camshaft (DOHC)
Dual overhead camshaft (DOHC) – An engine with two camshafts in each cylinder head, with one camshaft operating the intake valves and the other camshaft operating the exhaust valves. Also see Single overhead camshaft (SOHC).
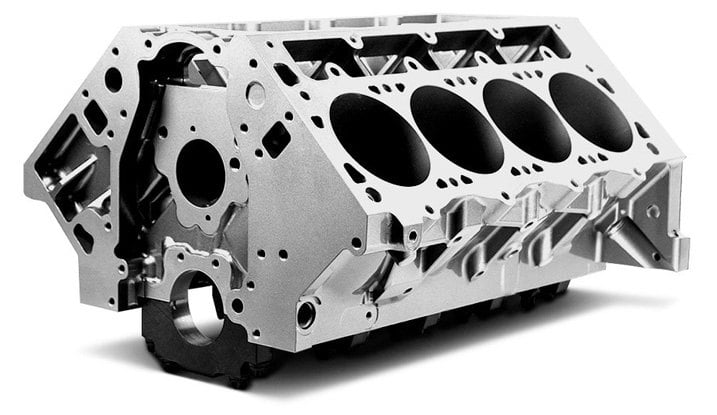
Engine Block
Engine block – The lower section of the engine, cast out of metal, which houses the cylinders, pistons, crankshaft, and other internal engine components.
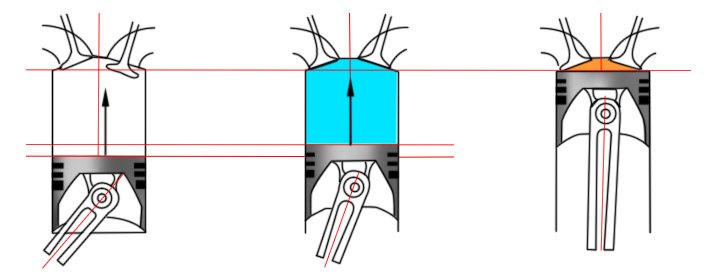
Engine Displacement
Engine displacement – a measurement of engine size based on volume inside all of the cylinders. The volume of a cylinder is the cylinder bore (distance across the center) multiplied by the length of the piston’s stroke. This number is then multiplied by the total number of cylinders to arrive at the total engine displacement figure – a number that’s expressed in liters, cubic centimeters, or cubic inches.
Exhaust Valve
Exhaust valve – A camshaft-driven valve in the cylinder head that opens to allow burned exhaust gases out of the cylinder after combustion.
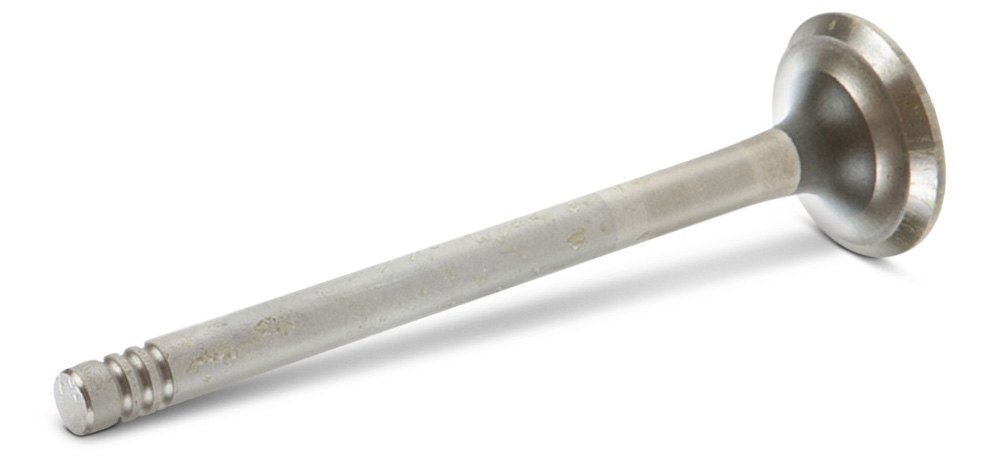

Expansion Plug
Expansion plug – A steel plug that fits snugly into an engine block opening to provide pressure relief if engine coolant expands and freezes (also known as freeze plug).

Flat Engine
Flat engine – an engine design with pistons that move horizontally rather than vertically. This type of engine will contain two separate sets of cylinder banks, both of which are laid out in a horizontal plane. This arrangement creates a flat-shaped block – giving the engine its descriptive name. As both sets of pistons share a crankshaft, they move in opposite directions. For this reason, flat engines are also described as “horizontally opposed” or “boxer” engines.

Four-Bolt Main
Four-bolt main – A crankshaft main bearing cap held in place by four bolts instead of the usual two to provide extra strength in high performance and racing applications.
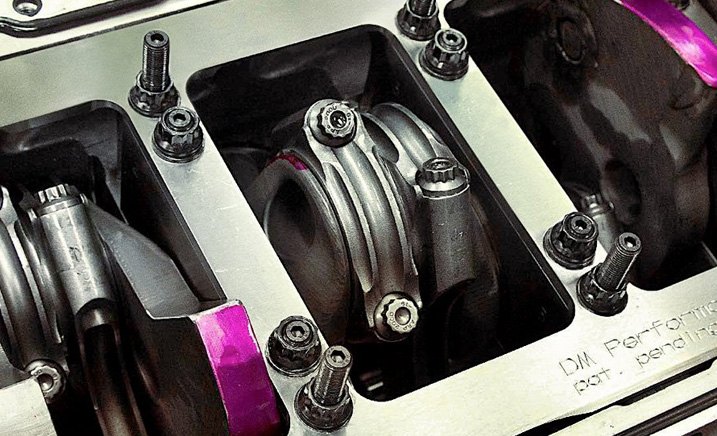
Four-Valve Cylinder Head
Four-valve cylinder head – An engine with two intake and two exhaust valves for each cylinder instead of one each.
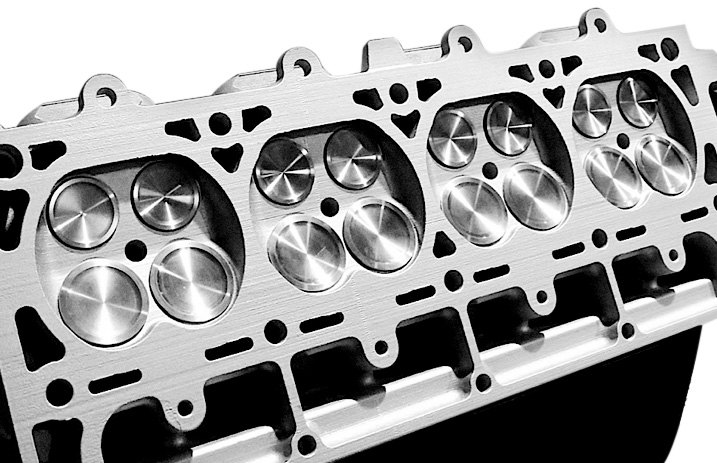

Head Bolts
Head bolts – see cylinder head bolts.
Hydraulic Valve Lifter
Hydraulic valve lifter – A valve lifter that uses hydraulic oil pressure to maintain zero valve clearance, reducing valve noise and eliminating the need for valve adjustments.
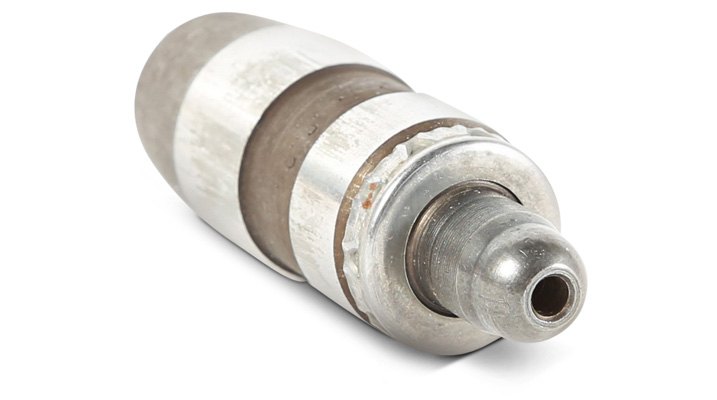

Intake Valve
Intake valve – A camshaft-driven valve in the cylinder head that opens only to allow the unburned fuel-air mixture into a cylinder before combustion.

Inline Engine Block
Inline Engine Block - If all cylinders are positioned in a row, one behind the other, you’ve got an inline engine. Most modern 4-cylinder engines and some 6-cylinder engines are laid out this way. Inline engines have one single cylinder head.
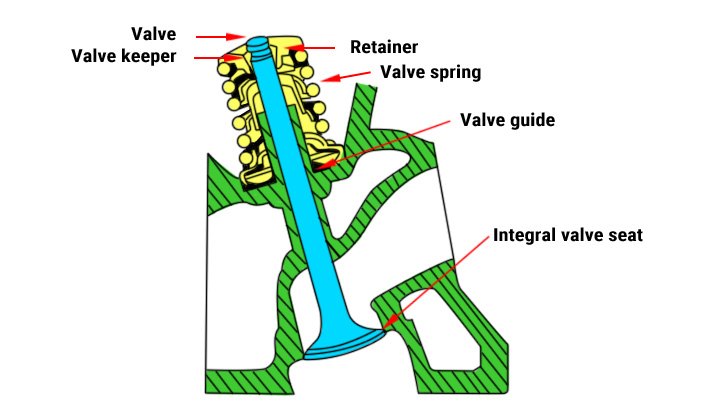
Integral Valve Seat
Integral valve seat – A valve seat that is machined into the cylinder head instead of a separate piece being inserted (also see valve seat).
Long Block
Long block – An engine block that’s fully assembled with internal components such as pistons, crankshaft, valvetrain, cylinder heads, and more. Long blocks do not include any fuel system connections (fuel injectors, fuel rails), electrical system components (spark plugs, coils, wires, distributor), or externally-mounted intake/exhaust system parts. “Long” does not refer to actual size or length of the engine block. See also short block.

Main Bearings
Main bearings – The bearings which are located between the crankshaft and the machined surfaces of the block. The crankshaft rotates on its main bearings.
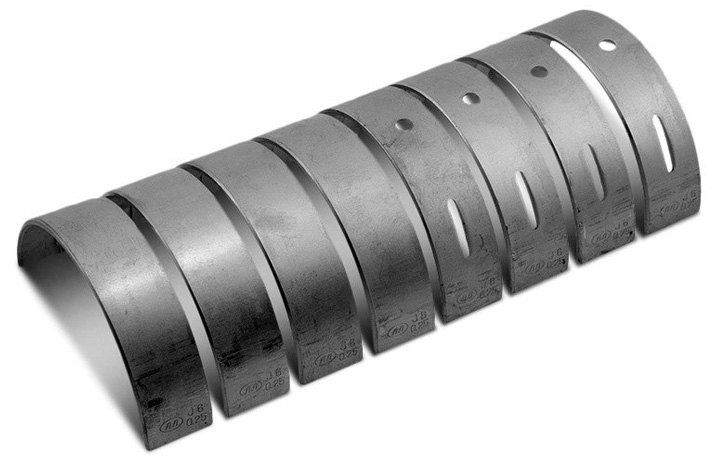

Main Bearing Caps
Main bearing caps – Removable, semicircular caps which bolt to the engine block to secure main bearings and the crankshaft in place.

Oil Control Ring
Oil control ring – A piston ring designed to control oil consumption within the cylinder (also see Piston rings).
Oil Galley Plug
Oil galley plug - A metal plug that’s threaded into a hole in the engine block casting.

Oil Pan
Oil pan – Bolted to the underside of the block, the oil pan encloses the crankshaft and serves as the engine's oil reservoir (also known as a sump).

Oil Pump
Oil pump – A pump that delivers oil to all moving internal parts of an engine.

Overhead Cam Engine
Overhead cam engine– An engine with a camshaft or camshafts located in the cylinder head(s) and above the valves.
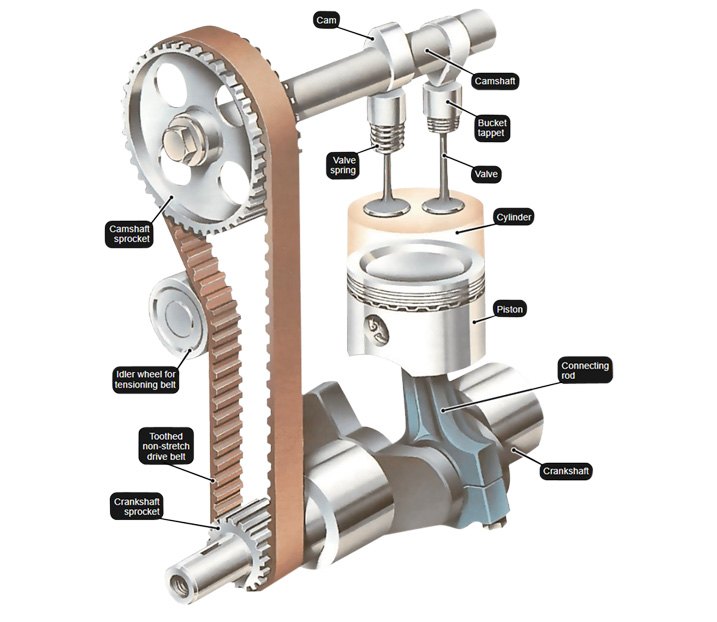
Overhead Valve Engine
Overhead valve engine – An engine with its camshaft located in the engine block, activating the valves in the cylinder head(s) through mechanical linkages.

Piston
Piston – A cylindrically-shaped metal piece that moves up and down within a cylinder of the engine block, and is attached to a connecting rod on its bottom side.

Piston Wrist Pin
Piston wrist pin – A cylindrical or tubular metal shaft that attaches a piston to a connecting rod.

Piston Pin Bushing
Piston pin bushing – A removable bushing that serves as a bearing surface for the piston pin.

Piston Pin Clip
Piston pin clip – A circular clip used at each end of a piston pin to secure it in place.

Piston Rings
Piston rings – Thin metal rings installed around the top of a piston that form a seal between the piston and the cylinder wall.

Push Rod
Push rod – A connecting link found in overhead valve engines that transfers motion of the camshaft in the engine block to the valve-actuating components in the cylinder head.

Push Rod Guide Plate
Push rod guide plate – Found on some older push rod engines, these are bolted in place and serve to keep the push rods moving in a straight path without wobbling. Some newer pushrod engines featured guides that are cast in place, and do not need bolt-on guide plates.

Push Rod Tubes
Push rod tubes – Found on older air-cooled engines, these are long hollow tubes that surround the push rods and serve as guide pieces.

Rocker Arm
Rocker arm – A lever driven by a pushrod or camshaft lobe which transfers motion to open and close the intake and exhaust valves. For various engines, we stock numerous rocker arm hardware pieces such as adjusting screws, balls & ball studs, nuts & bolts, bridges, oil baffles, pivot pieces, retainers, rocker arm shafts & hardware, and studs.
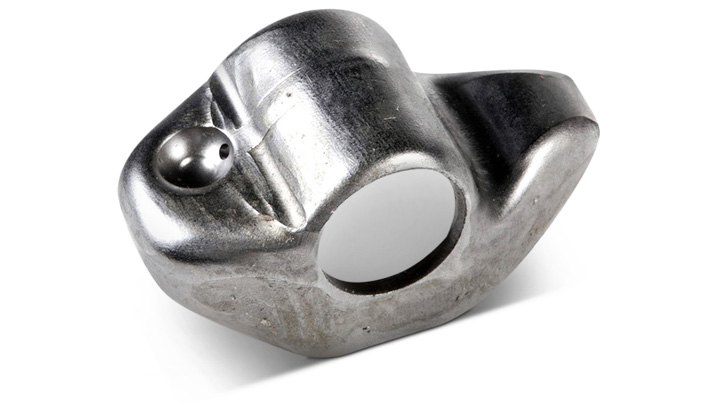

Rod Bearings
Rod bearings – The bearings which are located between the crankshaft and the connecting rods.

Short Block
Short block – An engine block that contains only basic internal moving parts, but not cylinder heads or oil pan. An older engine with camshafts inside the engine block will include said camshaft(s), timing gear, and balance shafts (if so equipped). Compared to a long block engine which is well-equipped, a short block is a bare-bones assembly. “Short” does not refer to actual length or size of the engine block.

Single Overhead Camshaft (SOHC)
Single overhead camshaft (SOHC) – An engine with one camshaft per cylinder head, with that camshaft operating both the intake and exhaust valves. Also see Dual overhead camshaft (DOHC).
Sleeve
Sleeve – see cylinder liner.
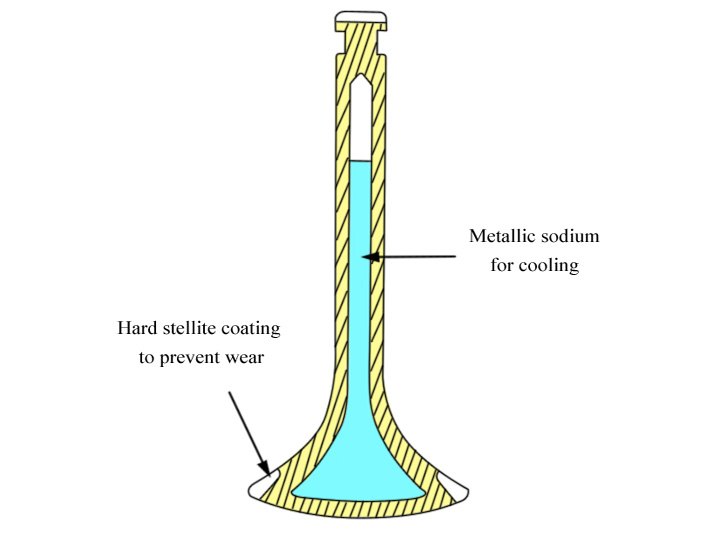
Sodium Cooled Valve
Sodium cooled valve – An exhaust valve with a hollow stem filled with sodium. When heated, the sodium melts and helps carry away heat, allowing the valve to operate at lower temperatures.
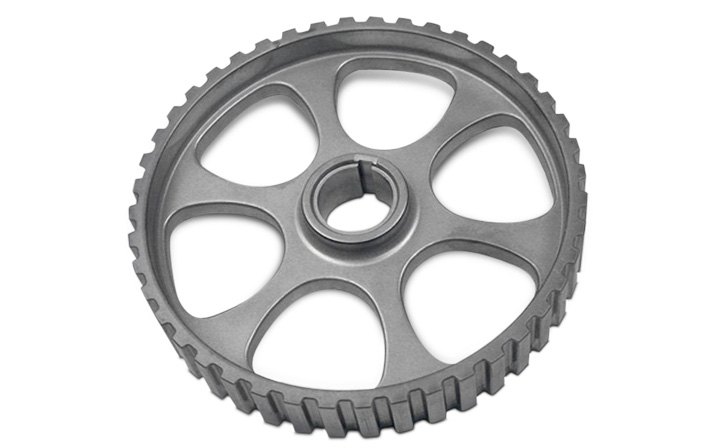
Sprocket
Sprocket – The set of teeth found around the outer circumferences of rotating wheels used to drive items such as a timing belt or chain.

Sump
Sump – see oil pan.
Tappet
Tappet – see valve lifter.
Timing Belt
Timing belt – A toothed belt made of reinforced rubber and riding on sprockets, which synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft with the rotation of the camshaft(s) so that the valves open at the appropriate time.

Timing Chain
Timing chain – A chain riding on sprockets, which synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft with the rotation of the camshaft(s) so that the valves open at the appropriate time.

Timing Gears
Timing gears – A set of gear wheels in direct mesh with each other, which synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft with the rotation of the camshaft(s) so that the valves open at the appropriate time.

V Engine
V engine - Most modern engines of 6 or more cylinders are laid out in a V configuration with 2 banks of cylinders. Half of the cylinders will be in the first bank, and half will be in the second bank. Because each bank of cylinders features its own cylinder head, a V engine is equipped with two separate cylinder heads.
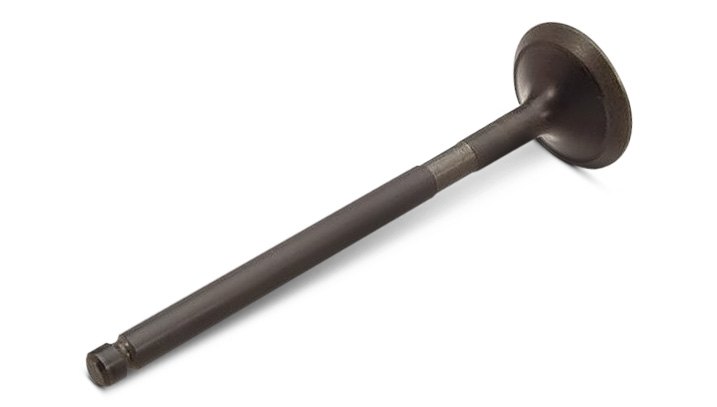
Valve
Valve – In an internal combustion engine, a device which opens to allow the passage of intake or exhaust gases, and closes in order to seal the combustion chamber.

Valve Cover
Valve cover – The piece which bolts on the top of a cylinder head, effectively serving as a protective lid.

Valve Cover Gasket
Valve cover gasket - A seal, typically made of rubber or cork, placed between a valve cover and cylinder head to prevent oil leakage.
Valve Guide
Valve guide – A cylindrically shaped opening in the cylinder head which serves as the channel for the valve stem as it moves up and down.

Valve Lifter
Valve lifter - A cylindrical piece, actuated by the camshaft, which transfers its motion to open an intake or exhaust valve (also known as cam follower or tappet).

Valve Seat
Valve seat – A surface, either machined into the cylinder head or pressed into place, against which the valve sits when it is closed.
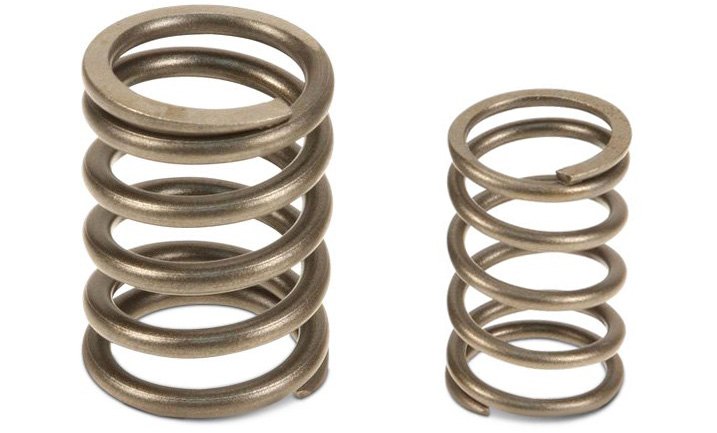

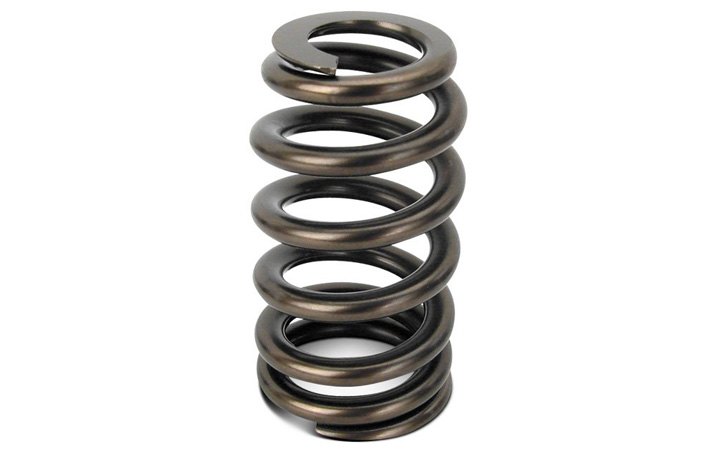
Valve Spring
Valve spring – A spring that keeps a valve closed, and against which the valvetrain must exert pressure when opening a valve.

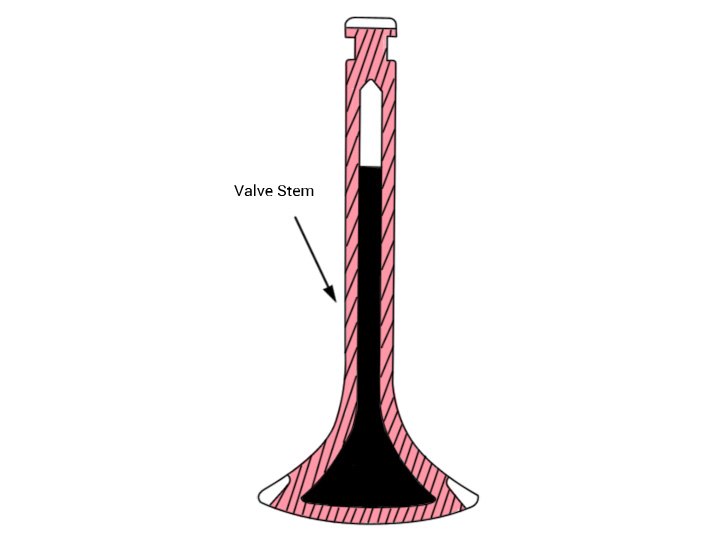
Valve Stem
Valve stem – The long cylindrical portion of a valve which moves up and down in the valve guide.
Valve Stem Seal
Valve stem seal – A round seal located between the valve stem and cylinder head to prevent oil in the cylinder head from leaking into the cylinder.

