Look up "fan belt" in any modern automotive dictionary, and you'll typically find a definition that reads, "An endless belt used to transmit power from a crankshaft-driven pulley to a pulley driving the fan, alternator, or other engine accessory. It is usually V-shaped in cross section with the point of the V fitting into a groove in the pulley".
Even though cooling fans on most modern vehicles are driven by electric motors instead of actual belts, the term fan belt is still incorrectly used as a blanket expression to describe any single accessory belt that may be used to drive a water pump, alternator, power steering pump, or other items. Why?

In order to pull cooling air through a vehicle's radiator, a cooling fan needs to be located at the front of the vehicle just behind the radiator. Traditional rear-wheel-drive vehicles with longitudinally-mounted engines had crankshaft pulleys right there at the front of the car, and they were convenient sources of power for cooling fans.
Since the fan belt tended to be the biggest and most noticeable one on the vehicle, the expression became universal for all other belts that looked similar – no matter what function they performed. Many original engine layouts also used that fan belt to spin water pump and alternator pulleys, and you may hear some people call it a "water pump belt" or "alternator belt" as well.
However, as vehicles with front-wheel-drive and sideways-mounted engines grew in popularity, the front of the engine was no longer at the front of the vehicle where the cooling fan was.


Engineers perfected electric fan motors, temperature sensors, and related computers to get the job done, and belt-driven fans were no longer necessary. Because cooling fans don't always need to be running at steady cruising speeds, electric motors which can shut off proved more energy efficient than direct drive belts which are always connected. Since electric cooling fans are used even in modern vehicles with longitudinally-mounted engines, the term fan belt has become virtually obsolete. More fitting terms to use when searching for a replacement single belt of this kind would be accessory drive belt or V-belt.
Because drive belts are subject to constant rotation, load, and heat, they are constructed in a similar fashion as tires. An outer layer of rubber surrounds internal steel and cord reinforcements to minimize stretching and maximize strength when grip is needed under load.
Accessory "V" Belts

Automotive accessory drive belts mounted visibly outside the engine are also known as "V-belts" because their trapezoidal shape tapers from wide to narrow as it forms a V point near the bottom. Tension on individual accessory belts is adjusted manually by tightening an adjuster to change the position of an idler pulley wheel, or by loosening and tightening slotted mounting brackets that move accessories such as an alternator by fractions of an inch.
As vehicle manufacturers added more accessories, their initial solution was to add more drive belts to power these accessories. So cars went from one belt driving the fan, water pump, and alternator, to 2 or 3 separate belts, now also driving the power steering pump, A/C compressor, and emissions air pump.
The "V" belt is one of the most effective solutions because of its strength, relative quietness, power transfer, and durability. The belt's ability to provide a small degree of slippage when needed makes it a good match for accessories that shut on and off by the use of a clutch, such as air conditioner compressors and older style radiator cooling fans.
Multi-Grooved Or Ribbed "V" Belts
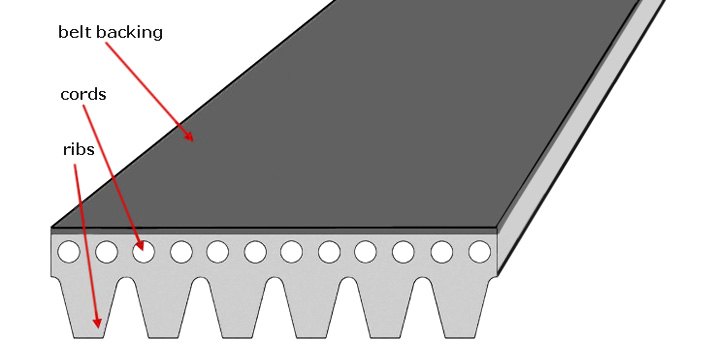
A variation on the above theme is provided by the so-called multi-grooved or ribbed belt. In practice, this is still a V-belt, but with smaller, multiple "V" shapes placed side-by-side. Its underside surface features endless parallel ridges designed to slot into mating grooves on the pulley to prevent sideways slippage. While this version of the V-belt is wider, it is also thinner, more flexible, and runs with less heat buildup. As load pressures increase on this type of V-belt, the rubber grooves wedge themselves further into the pulley and friction provides the necessary grip.
Serpentine Belts
Several factors have come together to change the way motor vehicle engineers have designed accessory drive belts. There has been an increased demand on accessories which derive their power from drive belts. At the same time, as vehicles have gotten smaller, engine compartments have become more crowded. Packaging of mechanical components into constricted spaces has become an important part of overall vehicle design.
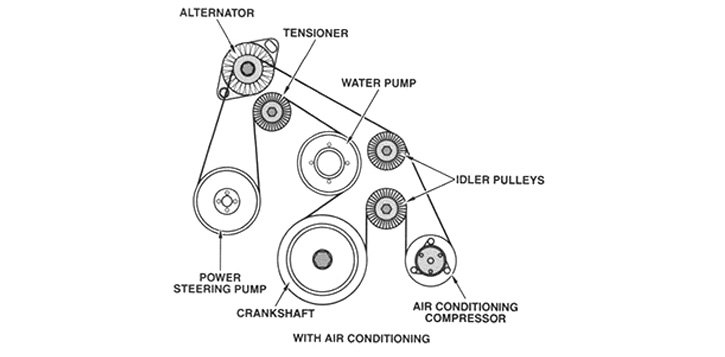
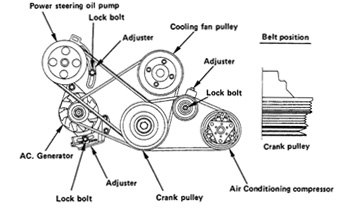
The above has led engineers to abandon the traditional V-belt in favor of a serpentine one, which is simply a longer version of a grooved V-belt. It may or may not have grooves on both sides. Instead of being specific to a single accessory, a serpentine belt is designed to wind around multiple pulleys – powering all of the vehicle's pulley-driven accessories. Depending on design, both sides of the belt may provide friction. Freewheeling "idler pulleys" are positioned in various locations in order to reroute the belt in the direction of the next accessory.
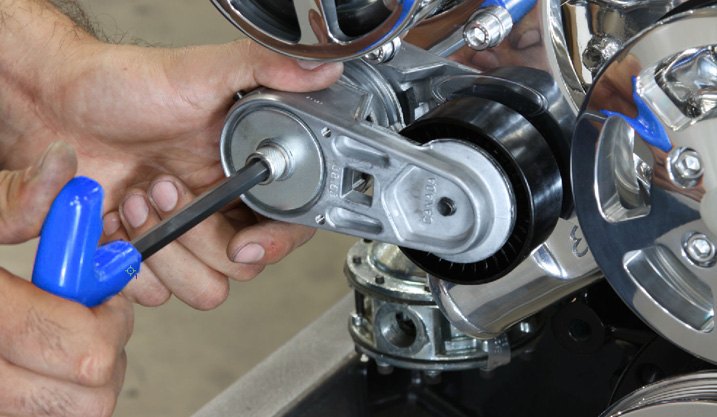

Unlike individual belts, tension on serpentine belts is provided by a tensioner pulley which is under constant spring pressure. The pulley never needs adjustment, and will release its tension when force is placed against it using a proper serpentine belt tool if the belt needs to be removed or replaced. Given the high quality of modern belts that can last from 60,000 to 100,000 miles, serpentine belt replacement is not a frequent procedure.
Timing Belts
"Are a drive belt and a timing belt the same?" is a popular question. Although both of them perform the drive function, timing belts should not be confused with accessory drive belts. Unlike drive belts that run accessories mounted on the outside of the engine, timing belts are encased inside the engine. They feature flatter construction with molded teeth, designed to mate with the teeth on the crankshaft and camshaft drive gears.
A spring-loaded pulley provides constant tension to ensure that this belt remains slip-proof so it maintains a fixed relationship among the gears for camshaft timing. Because of their necessity in engine operation, all timing belts have a fixed replacement interval (determined by the manufacturer.) Auxiliary drive belts are checked for wear and replaced when necessary.
As for the timing belt replacement cost, it's normally higher than the cost for serpentine belt replacement because of a somewhat more time-consuming job and the need to remove more parts. When timing belt replacement is performed, you also have to replace a spring-loaded pulley or tensioner and related hardware; the exact list depends on your engine model. If the timing belt is also used to drive the water pump, automakers recommend replacing the pump as well. We carry numerous kits containing all these parts, and they come from leading brands. For instance, the Aisin Timing Belt Kit is one of the most popular options.
Purchasing Replacement Accessory Belts
Whether it is sometimes referred to as a fan belt, alternator belt, or water pump belt, it is most properly called an accessory drive belt, V belt, or serpentine belt. Each vehicle has its own belt configuration, depending on its engine and optional accessories. When purchasing replacement belts, it is important to know your vehicle's year, make, and model, engine size, and in some cases, whether it is equipped with certain accessories such as air conditioning.
Some of the top brands offering quality drive belts are Bando, ACDelco, Dayco, Gates, and Continental. In order to improve their products, all of them implement the latest engineering solutions and achievements of the chemical industry, such as high-quality EPDM rubber, aramid fibers, or specially designed cords.
In particular, Bando is part of the Japanese corporation Bando Chemical Industries which has a great experience in rubber product manufacturing. The Bando Rib Ace series features a proprietary EPDM compound, oil- and heat-resistant backing, bidirectional cord to eliminate tracking, and other solutions aimed at a longer lifespan, quieter operation, better grip, resistance to stretching, and so on. The Bando Rib Ace V-Ribbed Serpentine Belt is one of the most popular products used in lots of modern vehicles by Kia, Hyundai, and Audi. Another widespread model of the Bando Rib Ace V-Ribbed Serpentine Belt can be found in many Japanese and Korean cars.
The ACDelco brand needs no introduction, as it's a famous supplier of OEM or aftermarket parts for pretty much any GM vehicle. The ACDelco GM Original Equipment V-Ribbed Serpentine Belt is very popular with the owners of Chevys, Cadillacs, GMCs, and Hummers. Another leader in the OEM equipment market is Dayco. Its Poly Rib Serpentine Belt features a highly effective aramid reinforced EPDM compound ensuring high durability and perfect resistance to cracking, heat, and stretching. It perfectly fits a wide range of Japanese and Korean vehicles.
Gates is another very serious player in the rubber industry, whose products set a high benchmark in terms of quality, efficiency, and longevity. Its assortment of belts is huge and covers virtually any vehicle that has at least one drive or timing belt. Particularly, the Gates Micro-V V-Ribbed Belt suits many Dodges, Jeeps, and some Japanese vehicles. And of course, many of us have heard about Continental, an old German manufacturer whose belts are famous for their long, trouble-free operation. The Continental ContiTech Conti-V Multirib Serpentine Belt is a shining example.
Given a great abundance of drive belts, many basic questions related to them are quite common. We answer some of the most frequent ones here:
FAQ
Where is a drive belt in a car?
In most front-wheel-drive cars with a sideways-mounted engine, one or several belts are located on the left side of the motor if you stand in front of your vehicle. If the motor is mounted longitudinally, the belt will be in front, behind the radiator.
Why is a drive belt squealing?
Typically, it is the result of improper tension. Other reasons include a worn-out, contaminated, or too long belt. If you hear squealing, inspect the belt itself and the parts responsible for its tension.
Which drive belt do I need?
Make sure you choose from the belts suitable for your engine model and vehicle configuration. Normally, a car with an air conditioner has a different belt than the same model without it. In a catalog, you will have to select the make, model, and year of your vehicle, along with other parameters if needed. Besides, you can check if your vehicle is present in the application list of a particular belt.
Is it time for drive belt replacement?
In most cars, this part lasts between 40,000 and 70,000 miles, but sometimes, its lifespan exceeds 100,000 miles. Typically, the belt should be replaced when it is cracked, worn out, or has other visual signs of damage. Also, you may consider drive belt replacement when the old belt has to be removed anyway, for instance, to complete other repair jobs under the hood.
Can a drive belt cause alternator failure or charging issues?
Actually, yes. If the belt's tension is too strong, it means a higher load on alternator bearings and a shorter lifespan. When the belt is too loose, it may slip, which negatively affects the belt itself, alternator efficiency, and charging the battery.

